DLNA Multimedia Server introduction
A multimedia server is an application that facilitates the sharing of multiple kinds of media through TNAS and smart devices via the DLNA protocol. Various kinds of media can be streamed on various devices as such servers can be used on TNAS, DLNA/UPnP devices, smart TVs, gaming consoles, web players and sound systems. Formats not listed above or any that may appear to not be functional with this application can also be converted via the transcoding feature. Installation is simple and the application can be located in the TOS Application Centre.
Overview
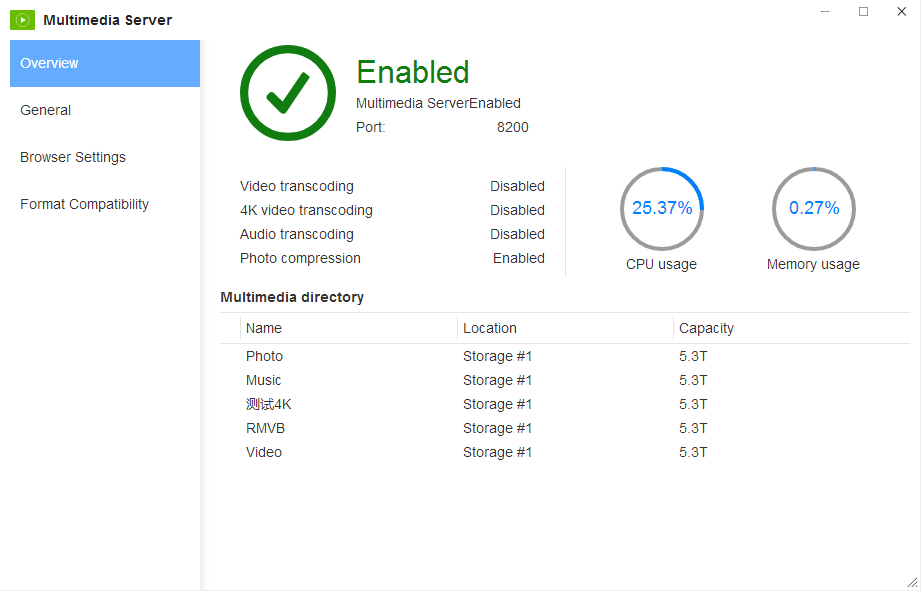
The ‘Overview’ page is located on the left-hand side of the home page and this page provides a breakdown of the key functions. For example, here is where data regarding CPU and memory usage can be found as well as how much storage us being utilized and whether video transcoding, 4K video transcoding, audio transcoding and photo compression are enabled.
General
The General page is where a log of multimedia items can be located and also where the port number and SSDP broadcast interval can be adjusted and the server can be switched on or off.
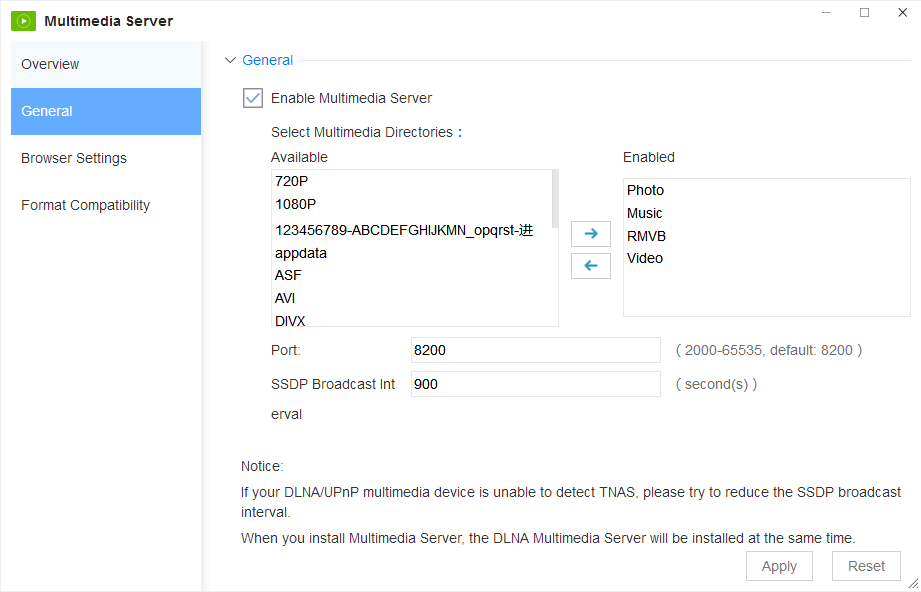
Select the ‘General’ tab on the multimedia after it has been started up to adjust the general settings.
After the multimedia server is installed, the initial state is off.
Powering up the multimedia server requires taking the steps listed below:
1.First, select the ‘Enable Multimedia Server’ option.
2.Transfer a shared folder from ‘Available Directories’ to ‘Enable Directories’ in order to attach the file to the multimedia directory.
3.The port number may also need to be reconfigured. For best results, the port number should be between 2000-65535. The port number is automatically set to the suggested number, 8200.
4.The SSDP broadcast interval allows DLNA/UPnP devices to perceive operating multimedia servers and is used by TNAS to emit broadcast signals to other DLNA/UPnP devices. It is automatically set to 900 but it can be reconfigured.
Save all reconfigured settings by pressing ‘apply’.
Note:
1.All multimedia files are kept in the Multimedia Directory and need to be moved to the Enabled Directory folder in order to be identified by the DLNA/UPnP device. Certain folders such as Video, Photo and Music folders, are automatically generated but more can be created and deleted.
2.Setting the SSDP to a lower broadcast interval will help the DLNA/UPnP device recognize TNAS If it is having problems. 900 is the automatic setting and the preferred setting.
Browse Settings
Multimedia servers facilitate the conversion of TNAS file to DLNA/UPnP devices and the settings for viewing images, video and hearing audio are adjustable.
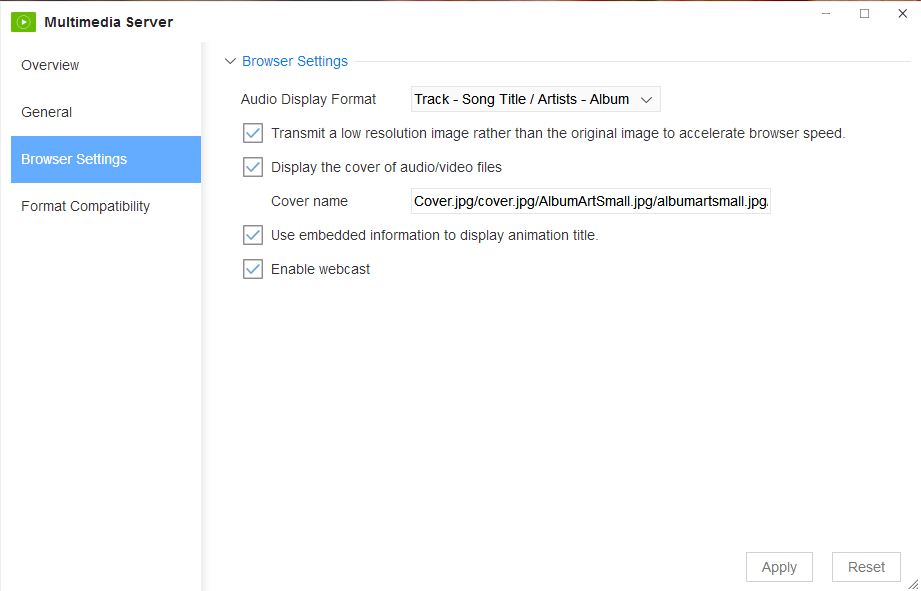
The ‘Browse Settings’ tab is where many of the multimedia server functions can be adjusted to preferred setting.
1.Click on the ‘Music Display Format’ tab in order to reconfigure the way in which the titles of music selected to be played will be displayed. There is a choice of five styles: ‘Show song name only’, ‘Track-title’, ‘Song name/album’, ‘Song name/actor’, ‘Track-title/actor-album’.
2.Select ‘Transfer low resolution images instead of original images’ in order to peruse the images faster.
3.The cover page for audio and video can be altered by selecting ‘Show audio/video cover page’ and changing the file name to your choice.
4.Select ‘Use inline information to display the animation title’ in order to show the animation title.
5.The webcast is automatically configured to ‘Enable webcast’ but it can be disabled. When the webcast is disabled the TNAS multimedia server will not be identified by the DLNA/UPnP device.
Pressing ‘Apply’ will save any reconfigured settings.
Note:
1.It is only possible to reconfigure the album art of music files that do not have embedded pictures. Embedded files will not be replaced.
2.Files for cover pages that have been newly created must be saved to a music sharing folder.
3.The data embedded in the multimedia file determines how or if an animated title will be shown.
Format Compatibility
By enabling audio / video transcoding, files that may have been more difficult to convert can be made into compatible formats for better streaming. The quality of the DLNA player will determine the quality of the audio or video being streamed. If the player does not support the chosen file format, this can be adjusted in the ‘Format Compatibility’ tab.
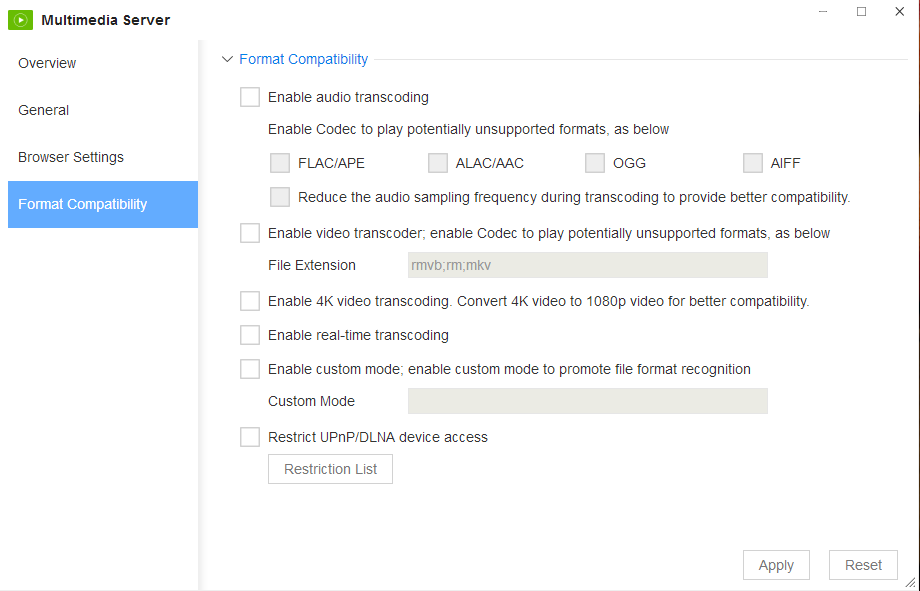
It is possible to reconfigure the compatibility configurations by selecting ‘Format compatibility’ and taking the following steps:
1.‘Enable audio transcoding’ will allow the DLNA/UPnP to use audio formats that it have may not been otherwise able to sustain.
2.Select ‘Reduce the sample rate audio frequency when transcoding to provide better compatibility’ to decrease the bit rate of the audio and make it better suited to the device.
3.For video files that may not be compatible with the DLNA/UPnP device, select ‘Enable video transcoder’ to convert the video file to another extension. Use a semi-colon to separate multiple extensions.
4.4K videos can be transcoded to 1080P video by selecting ‘Enable 4K video transcoding’.
5.Select ‘Enable real-time transcoding’ to stream live media to the DLNA/UPnP device.
6.Select ‘Enable custom mode’ to allow the TNAS a wider recognition pool of file formats and enter a custom format to further help the TNAS identify the various file types. E.g. for an xxx.abc audio file type abc=audio/x-audio. For an xxx.cdevido file type cde=video/x-video.
7.‘Restrict DLNA/UPnP device access’ can be used to prevent the DLNA/UPnP device’s ability to identify the TNAS.
Pressing ‘apply’ will save all configurations.
Note:
1.Enabling the audio transcoder allows TNAS to convert audio files with the FLAC / APE, ALAC / AAC, OGG, AIFF formats to MP3 files. Selecting ‘real-time transcoding’ will allow the DLNA/UPnP device to convert files as they are being streamed.
2.Selecting ‘Enable video transcoder’ without selecting ‘Enable real-time transcoding’ will convert unsuitable video files to a 1080P resolution MP4 file to be placed in the same folder as the multimedia file.
More information on transcoding formats for TNAS models in different devices can be found here.
